
Toyota is one of the world's largest and most successful automobile manufacturers. Today, the company produces a wide range of vehicles, from compact cars to luxury SUVs, and is known for its commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability. However, before 1944, Toyota's history was very different.
The company was founded in 1933 by Kiichiro Toyoda, the son of Sakichi Toyoda, an inventor and industrialist who had developed a number of innovations in the textile industry. Kiichiro Toyoda was interested in automobiles, and he believed that Japan could build a competitive car industry if it focused on producing small, affordable vehicles.
To that end, Toyoda established the Toyota Motor Company and began working on a small car that would be affordable for the average Japanese consumer. The first prototype was called the A1, and it was powered by a small gasoline engine. However, the company quickly realized that it needed to develop a more advanced engine to compete with foreign manufacturers.
As a result, Toyoda and his team began working on a new engine that would be more powerful and efficient than anything else on the market. This engine, called the Type A, was a four-cylinder engine with a displacement of 1.5 liters. It was designed to be lightweight and efficient, and it quickly became the heart of Toyota's first production car, the Model AA.
The Model AA was introduced in 1936, and it was an instant success. It was small, affordable, and reliable, and it quickly became one of the most popular cars in Japan. However, the company soon realized that it needed to develop a more advanced car to compete with foreign manufacturers.
To that end, Toyoda and his team began working on a new car that would be more powerful and luxurious than anything else on the market. This car, called the Model AB, was powered by a new engine called the Type B. It was a six-cylinder engine with a displacement of 2.0 liters. It was designed to be powerful and efficient, and it quickly became the heart of Toyota's second production car, the Model AB.
The Model AB was introduced in 1940, and it was an instant success. It was larger, more luxurious, and more powerful than the Model AA, and it quickly became one of the most popular cars in Japan. However, the company soon realized that it needed to develop a more advanced car to compete with foreign manufacturers.
To that end, Toyoda and his team began working on a new car that would be more advanced and luxurious than anything else on the market. This car, called the Model AC, was powered by a new engine called the Type C. It was a six-cylinder engine with a displacement of 2.5 liters. It was designed to be powerful and efficient, and it quickly became the heart of Toyota's third production car, the Model AC.
The Model AC was introduced in 1944, and it was an instant success. It was larger, more luxurious, and more powerful than the Model AB, and it quickly became one of the most popular cars in Japan. However, the company soon realized that it needed to develop a more advanced car to compete with foreign manufacturers.
Overall, before 1944, Toyota was still in its early days and primarily focused on producing small, affordable cars for the average Japanese consumer. The company's founder Kiichiro Toyoda had a vision to build a competitive car industry in Japan and was focused on developing advanced and efficient engines. The company's first three production cars, the Model AA, AB, and AC were all successful in their own right and laid the foundation for Toyota's future success.
In the immediate aftermath of World War II, Toyota was in a difficult position. The company's factories had been heavily damaged during the war, and it was struggling to produce cars at the same level as before. Despite these challenges, Toyota's management team was determined to rebuild the company and make it one of the leading car manufacturers in the world.
One of the key challenges that Toyota faced during this period was the lack of resources. The company had to make do with limited materials and manpower, which made it difficult to produce cars at the same level as before the war. However, Toyota's management team was able to come up with innovative solutions to these problems, such as using cheaper materials and developing new manufacturing techniques.
Despite these difficulties, Toyota was able to produce its first post-war car, the SA model, in 1947. This car was a hit with consumers, and it helped to establish Toyota as a major player in the car industry. Over the next few years, Toyota continued to develop and improve its cars, and it quickly became one of the most respected car manufacturers in the world.
In the 1950s, Toyota began to expand its operations beyond Japan. The company opened its first overseas factory in Brazil in 1959, and it soon began to export cars to other countries around the world. This expansion helped Toyota to become a global car manufacturer, and it helped to establish the company as a major player in the international car market.
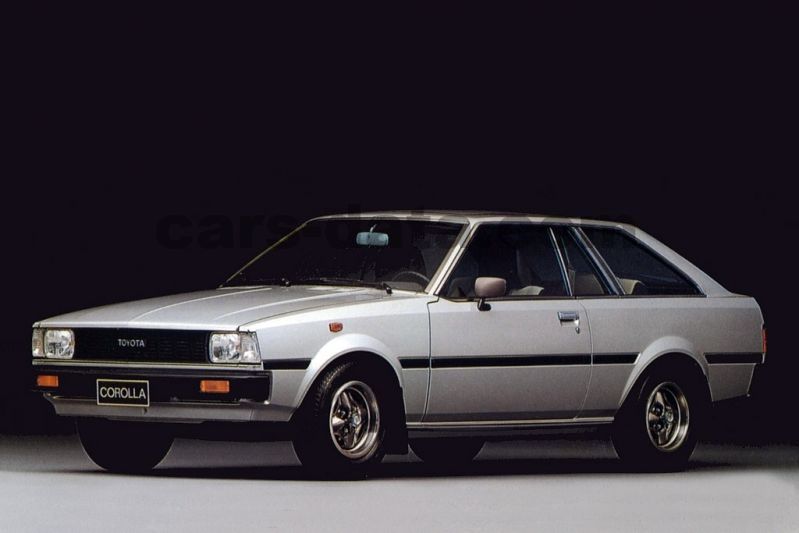
In the 1960s, Toyota continued to expand its operations and improve its cars. The company introduced the Corolla model in 1966, which quickly became one of the best-selling cars in the world. Toyota also began to invest in new technologies and manufacturing techniques, such as automation and robotics, which helped to improve the efficiency and quality of its cars.
In the 1970s, Toyota faced a new set of challenges as the global car market began to change. The company had to adapt to new trends, such as the rise of smaller and more fuel-efficient cars, as well as increased competition from other car manufacturers. Despite these challenges, Toyota was able to continue to grow and innovate, and it remained one of the most respected and successful car manufacturers in the world.
In the 1980s, Toyota continued to expand its operations and improve its cars. The company introduced the Camry model in 1983, which quickly became one of the best-selling cars in the world. Toyota also began to invest in new technologies and manufacturing techniques, such as automation and robotics, which helped to improve the efficiency and quality of its cars.
In the 1990s, Toyota faced a new set of challenges as the global car market began to change. The company had to adapt to new trends, such as the rise of smaller and more fuel-efficient cars, as well as increased competition from other car manufacturers. Despite these challenges, Toyota was able to continue to grow and innovate, and it remained one of the most respected and successful car manufacturers in the world.
In the 2000s, Toyota faced a new set of challenges as the global car market began to change. The company had to adapt to new trends, such as the rise of smaller and more fuel-efficient cars, as well as increased competition from other car manufacturers. Despite these challenges, Toyota was able to continue to grow and innovate, and it remained one of the most respected and successful car manufacturers in the world.
Today, Toyota is one of the most respected and successful car manufacturers in the world. The company continues to produce high-quality cars that are loved by consumers around the world. It has also invested heavily in new technologies, such as electric and hybrid cars, to ensure that it remains at the forefront of the automotive industry.
In recent years, Toyota has also focused on sustainability and reducing its environmental impact. The company has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon emissions and promote more sustainable practices throughout its operations. This has helped Toyota to maintain its reputation as a responsible and innovative car manufacturer.
Overall, Toyota's history after 1944 has been one of overcoming challenges, innovation and expansion. Despite the difficulties it faced in the aftermath of World War II, the company has managed to become one of the most respected and successful car manufacturers in the world. With a strong focus on innovation and sustainability, Toyota is well-positioned to continue to be a leader in the automotive industry for many years to come.
Toyota vin tag
